Bert
The BERT is the most important achievement in the NLP field in the last 4 years. It makes the transfer learning of NLP tasks possible and the transformer framework dominant the NLP field.
This is a series of paper reading notes, hopefully, to push me to read paper casually and to leave some record of what I've learned.
Paper link: Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding
Useful links: https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PL411M7eQ
https://youtu.be/UYPa347-DdE
Deep contextualized word representations - arXiv
Notes by sections
0. Abstract
The name of BERT might come from one of its important related work, ELMo. And Elmo and Bert are both characters in a TV show Sesame Street.
The abstract focus on the two related work, ELMo and GPT. The bidirectional feature is in contrast to the unidirectional GPT model. And the "without substantial task specific architecture modifications" feature compares with the RNN-based ELMo model, whose architecture might get modified when training downstream tasks. Yet the ELMo model is bidirectional and GPT model is easy to use.
When claiming a model is great, it is good to provide both the absolute accuracy and the relative accuracy compared with others. Just like this paper does.
6. Conclusion
To summarise, this is a classical A+B type of research. The idea of BERT is simple, combine the advantages of the bidirectional network with a rather old RNN base (ELMo), and the unidirectional network with a transformer base (GPT). And in detail, 2 pre-training tasks are designed.
The main contribution of this network is showing that bidirectional information is important.
1. Introduction
From the history introduction, it turns out BERT is not the first to apply pre-training on NLP. It's been a while. But BERT makes it popular.
2. Related work
2.3 Transfer Learning from Supervised data
This is what the CV area does most often. Yet it is not effective in NLP. It is partly because of the lacking of data. Another reason might be the existing labeled data focus only on language inference and machine translation, which are too different from other NLP tasks. So BERT and GPT use unlabelled data to pre-train and prove that unsupervised pre-train on a massive data is more effective than supervised pre-train on a relatively small data set. And, interestingly, this trend in NLP gradually effects the CV world. Nowadays unsupervised fine-tuning is becoming more and more popular in CV area.
3. Bert
In the first part, the pre-training and fine-tuning framework is briefly covered. A paper should be self-consistent, meaning that if a mechanic is fundamental in your area and essential to your work. It is a good habit to briefly introduce it, even if all the people in the area know it.
Model Architecture
And the architecture is as simple as just take the encoder part of the transformer model.
number of layers (i.e., Transformer blocks) as L, the hidden size as H, and the number of self-attention heads as A.
BERTBASE(L=12, H=768, A=12, Total Parameters=110M) and BERTLARGE(L=24, H=1024, A=16, Total Parameters=340M).
Because the hidden size of each multi-head attention sublayer is set as 64. And in transformer tradition, H = A * 64. So the multi-head number A actually depends on the hidden size H. As a result, the way of calculating the number of parameters is shown below.
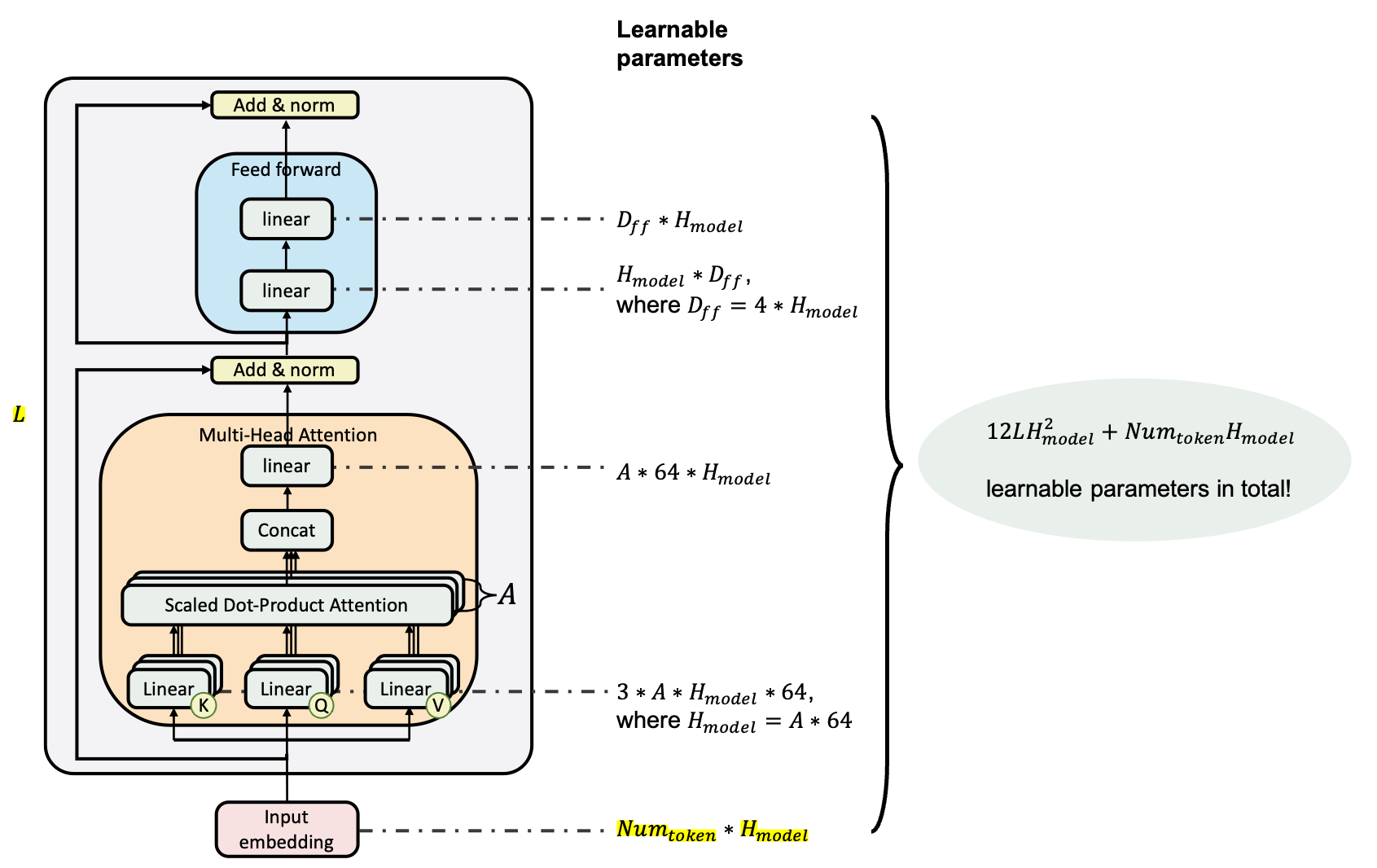
Input/Output Representations
Why Bert need a pair of sentence to handle downstream tasks such as Machine Translation, unlike its predecessor Transformer?
Because in Transformer, the input is a pair of sequences, taken by encoder and decoder respectively. But Bert is only an encoder. In English-Chinese Translation task for example, for transformer, the encoder take the English version and the decoder take the Chinese version, for Bert, the English version and Chinese version are glued with a special token [sept] then be inputed to the model.
Besides the [sept] token, another embedding is introduced into the embedding layer, the sequence model. Details are shown below.
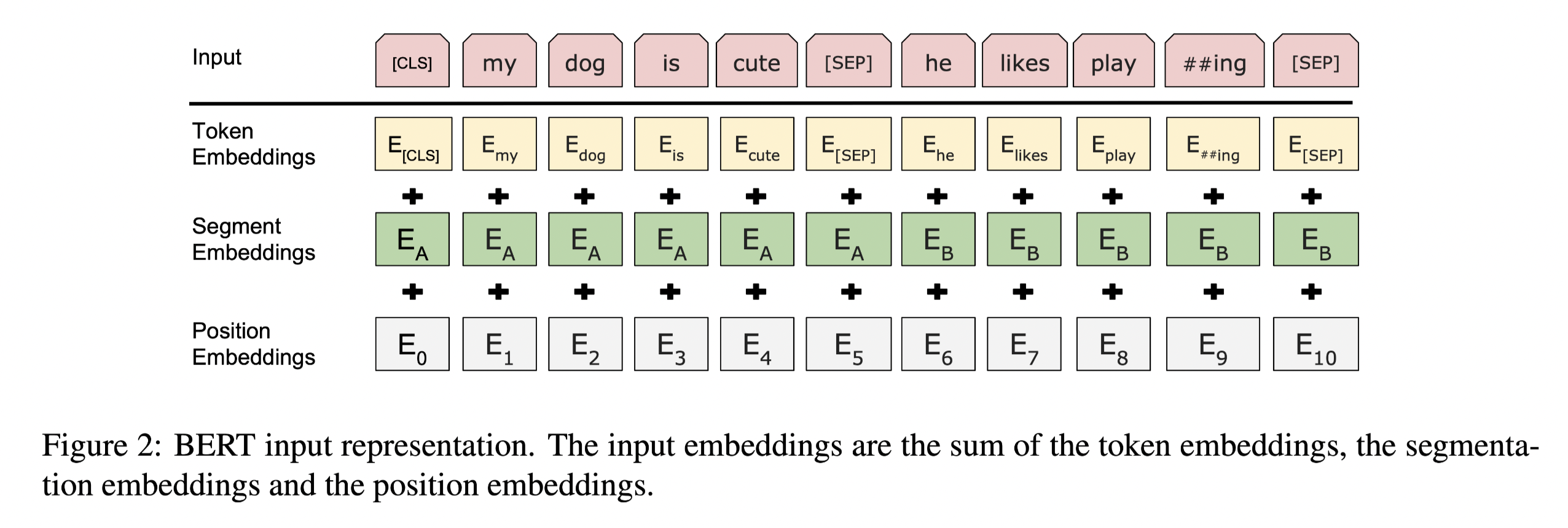
3.1 Pre-training BERT
The paper provides an example of each task in Appendix section Masked LM and the Masking Procedure, just go for it and have a look if don't understand.
Next Sentence Prediction The next sentence prediction task can be illustrated in the following examples.
Input = [CLS] the man went to [MASK] store [SEP] he bought a gallon [MASK] milk [SEP]
Label = IsNext
Input = [CLS] the man [MASK] to the store [SEP] penguin [MASK] are flight ##less birds [SEP]
Label = NotNext
The "flight ##less" is because of the WordPiece embedding method that Bert uses. "##" means this token is split from last token, in this case, flightless is the original token. Because flightless is rarely used, the WordPiece embedding split this word into two.
3.2 Fine-tuning BERT
Bert's architecture has one advantage over the transformer's, the self-attention allows model look both the two sentences. And the encoder-decoder model can't do that. As a result, the fine-tuning can be a little bit hazy.
4 Experiments
4.2 SQuAD v1.1
We fine-tune for 3 epochs with a learning rate of 5e-5 and a batch size of 32.
This misleads the people for a while. People found when fine-tuning with Bert, the variance of each results are high i.e. the result of fine-tuning is unstable. Then people found it is because 3 epochs are not enough. Besides, the optimiser that the original Bert model used is an incomplete version of Adam which is not stable for small epoch number. And the follow-ups change it into the original Adam.
From the processes of the 3 experiments, it can be seen it is easy for BERT to be applied to downstream tasks. Just need to modify the input data in the form of the Bert sequence, and add another output layer. As a result, with BERT, massive number of tasks can be trained under a rather simple architecture.
5 Ablation Studies
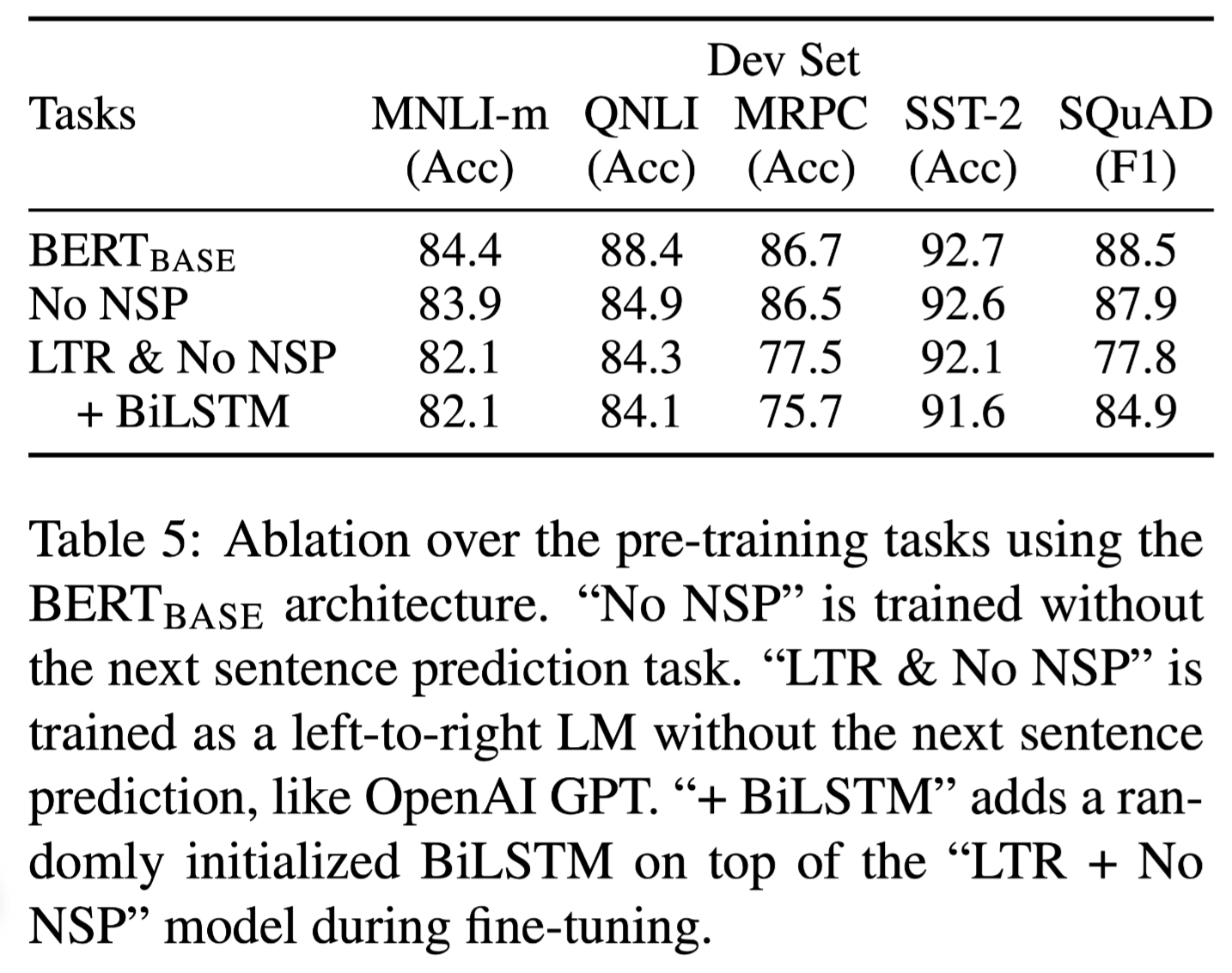
It is obvious the 4th architecture BiLSTM is from the idea of ELMO. And all the variation lead to a deterioration of the acc, especially in the MRPC task.
Microsoft Research Paraphrase Corpus (MRPC) Dataset
Created by Dolan et al. at 2005, the Microsoft Research Paraphrase Corpus (MRPC) Dataset contains pairs of sentences which have been extracted from news sources on the web, along with human annotations indicating whether each pair captures a paraphrase/semantic equivalence relationship., in English language. Containing 5,8 in Text file format.
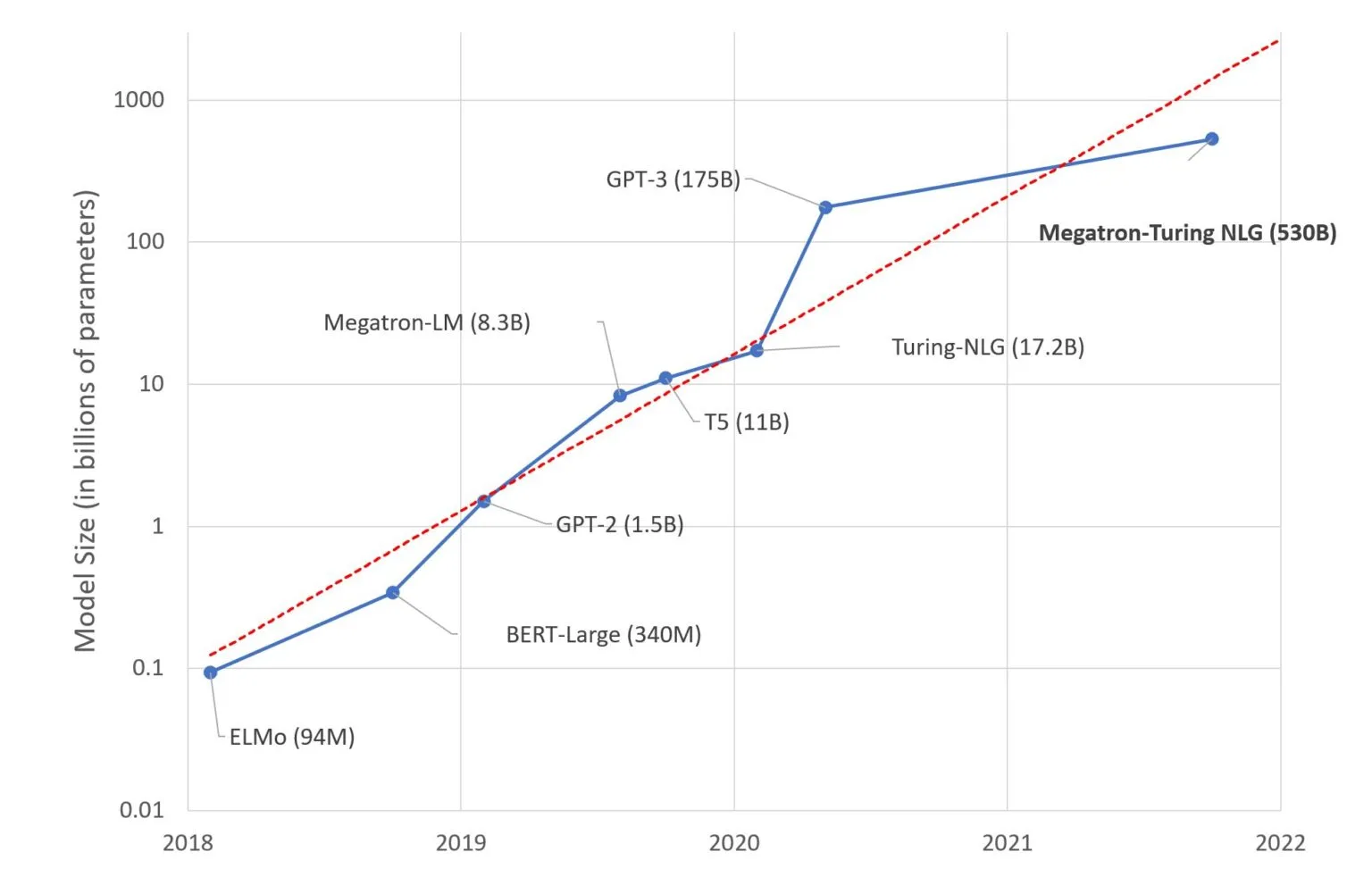
In the Effect of model size part, they claim with a large model size, huge improvement can be reached. And this leads a trend of increasing the model size in NLP, for example, the 100 billon GPT-3, and 500 billion model Megatron-Turing Natural Language Generation (MT-NLG). The boundary of NLP will be push further.
Reviews
Writing: The biggest sell point in this paper is chosen as the "bidirectional". From today's view, the contributions of BERT are so more than this. Besides, when say to choose a feature, it is better to discuss both the pros and the cons of the choice. For example, compared with GPT, the encoder is used instead of the decoder. The pros are the bidirectional feature, but the cons is the resulting difficulty in applying on generative tasks such as the machine translation.
Besides, BERT follows a whole ideal path of solving deep learning problems. That is after pre-training on a deep and huge model on a huge unlabelled dataset, the model can be applied to many small tasks with a few steps of fine tuning.